Have you ever pushed your body to its limit, only to wake up the next morning with sore muscles that make every movement painful? You’re not alone. Sore muscles are a common issue for anyone who engages in physical activity, whether you’re a seasoned athlete or a weekend warrior. But what’s the best way to alleviate that discomfort?
Some swear by heat therapy, while others insist that cold therapy is the way to go. So, which one is it? Ice is ideal for acute injuries, while heat is better for chronic pain. Both therapies can relieve muscle aches and pains.
In this article, we’ll explore the science behind muscle recovery, and dive into the pros and cons of each therapy. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of which therapy is best for your sore muscles, and how to apply it for maximum relief. So, grab a seat and get ready to learn!
The Role of Temperature in Muscle Recovery
Muscle recovery is a complex process that involves repairing damaged muscle fibers and reducing inflammation. Temperature can play a crucial role in this process, as it can affect blood flow to the affected area and the rate at which metabolic waste products are removed from the muscles.
When muscles are damaged during exercise, they release metabolic waste products such as lactic acid, which can contribute to soreness and inflammation. Applying heat to the affected area can increase blood flow to the muscles, which can help flush out these waste products more quickly. Increased blood flow also delivers oxygen and nutrients to the muscles, which can promote healing.
Cold therapy, on the other hand, can help reduce inflammation and numb the area, which can provide temporary relief from soreness.
Cold therapy works by constricting blood vessels in the affected area, which can reduce the flow of blood and other fluids to the area. This can help reduce inflammation and swelling, which can alleviate pain and promote healing.
Which Therapy is Better for sore muscles
The ideal temperature range for muscle recovery will depend on the type and severity of the injury. For acute injuries, such as strains or sprains, ice is typically recommended to reduce swelling and inflammation.
Heat is generally more effective for chronic or long-term pain, as it can help promote blood flow and relaxation of tense muscles.
It’s important to note that temperature therapy should be used in conjunction with other strategies for muscle recovery, such as rest, hydration, and stretching. If you’re experiencing severe or persistent muscle pain, it’s best to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment.
What helps sore muscles fast?
Sore muscles can be a frustrating experience, as they can limit your mobility and make even simple tasks difficult. Fortunately, there are several strategies that can help relieve sore muscles quickly.
Rest
One of the best ways to alleviate sore muscles is to take a break from the activity that caused the pain. Resting the affected muscles allows them to recover and repair.
Hydration
Drinking plenty of water or oral salts can help flush out metabolic waste products that build up in the muscles during exercise, which can contribute to muscle soreness.
Massage
Massaging sore muscles can increase blood flow to the affected area, which can help speed up the healing process.
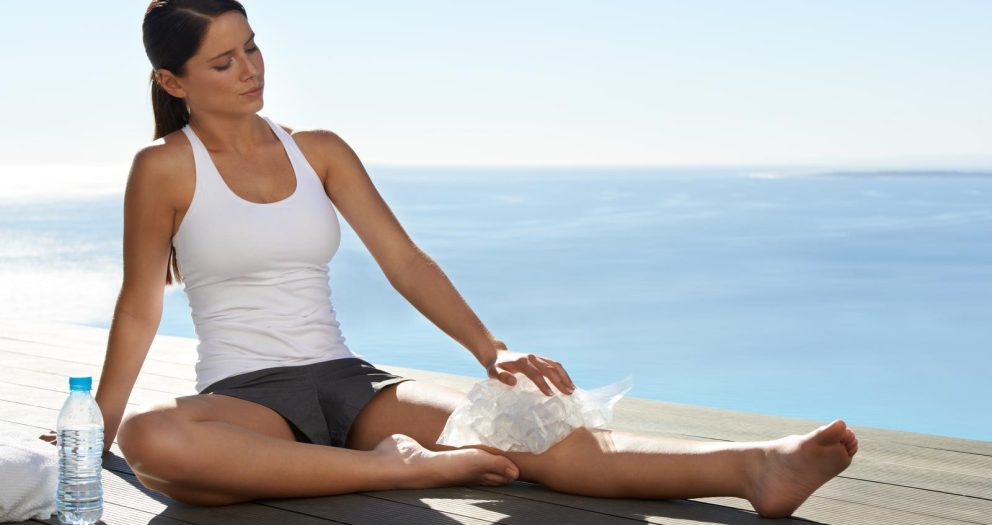
Heat therapy
Applying heat to sore muscles can help increase blood flow to the area, which can promote healing and relieve pain.
Cold therapy
Cold therapy can help reduce inflammation and numb the area, which can provide temporary relief from soreness.
Stretching
Stretching can help relieve muscle tension and reduce stiffness, which can alleviate soreness.
Over-the-counter pain medication

Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
It’s important to note that the best way to relieve sore muscles will depend on the cause and severity of the pain. If you’re experiencing severe or persistent muscle pain, it’s best to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment.
References
- Mayo Clinic – https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/fitness/in-depth/exercise/art-20048389
- Harvard Health Publishing – https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/sore-muscles-dont-stop-exercising
- American College of Sports Medicine – https://www.acsm.org/docs/default-source/files-for-resource-library/treating-muscle-soreness.pdf?sfvrsn=ca12eb0c_4
- National Institutes of Health – https://www.nih.gov/news-events/nih-research-matters/massage-muscle-soreness
- WebMD – https://www.webmd.com/fitness-exercise/features/sore-muscles-dont-stop-exercising#1